Many people seek for ways to expand their awareness as part of their journey toward self-realization and spiritual development. Psychedelics have been used by many different societies throughout time to achieve heightened levels of awareness and gain new spiritual perspective. In recent years, there has been an upsurge in the use of various psychedelics for therapeutic and exploratory purposes. To many people’s surprise, there are way more psychedelic substances available to humanity than one could imagine. In this guide, we will discuss the 9 most popular psychedelics, their effects, and their potential applications for personal growth and healing. Read it and see if you learn anything new!
Psilocybin: Discovering the Mystical World of Magic Mushrooms
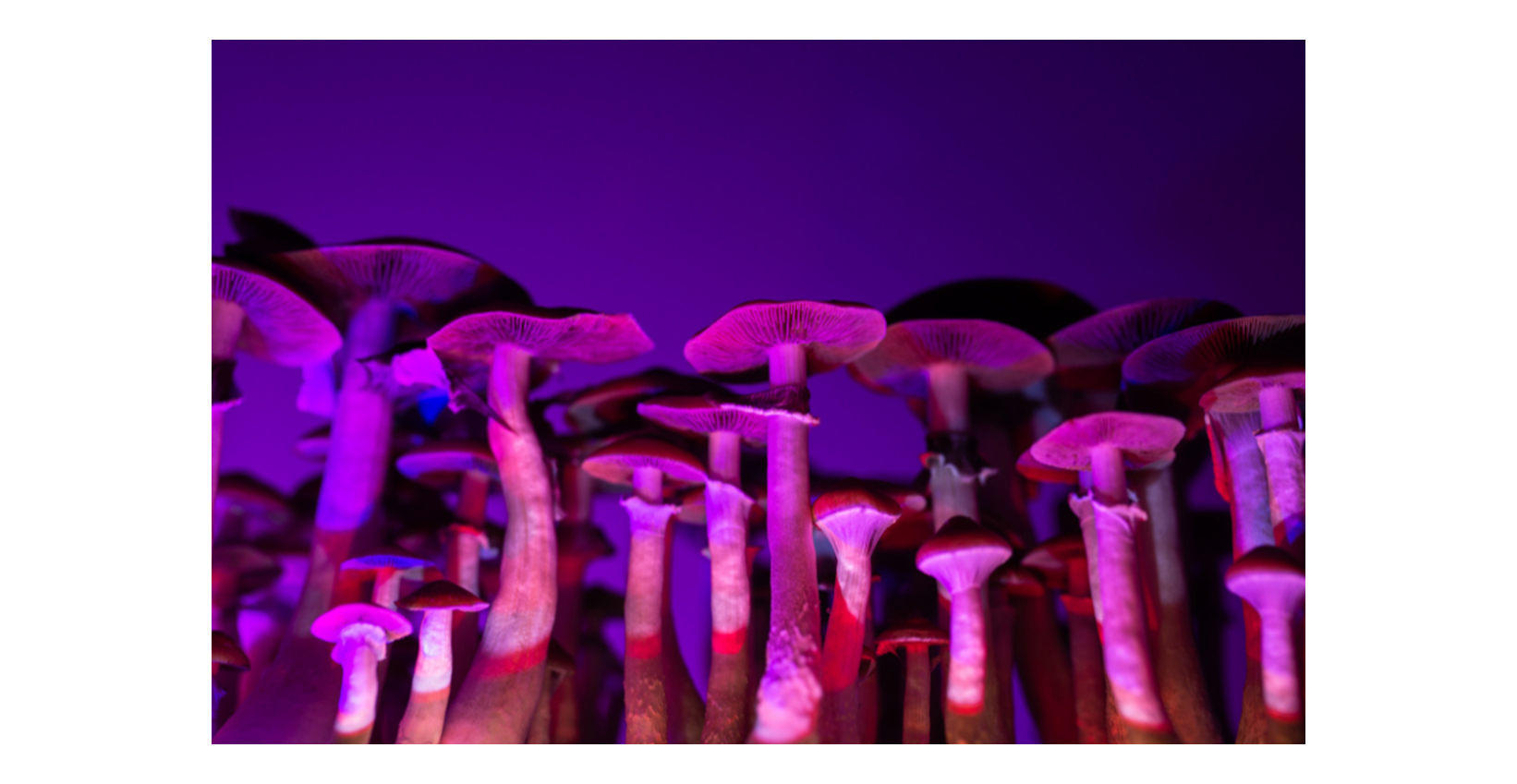

Psilocybin, the extraordinary compound found in magic mushrooms, has long been used by indigenous cultures as a sacred tool for spiritual exploration and self-discovery. It is undoubtedly one of the most popular psychedelics out there. Its effects can include increased awareness, euphoria, vivid hallucinations, and a profound sense of connection with the universe.
The barriers between self and other dissolve, revealing the interconnectedness of all things. In these moments of unity, it becomes possible to gain deep insights into your own psyche, resolve internal conflicts, and potentially heal emotional wounds. A psilocybin trip lasts anywhere from 4-6 hours, and the intensity of experience can come in ‘waves’. The trip can offer a glimpse into a world where the mystical and the scientific worlds merge, where the boundaries of our understanding are pushed, and where the impossible becomes possible. Therefore, psilocybin is best suited for self-exploration, mystical or spiritual experiences, changing thinking patterns, and looking to learn a new perspective on things. It has been long used in human history by various cultures for religious, spiritual, and healing purposes.
LSD: Revolutionary Potential of the Human Mind

Lysergic acid diethylamide, or LSD, is a potent synthetic psychedelic that gained popularity in the 1960s. Known for inducing intense visuals, deep introspection, and feelings of unity, LSD has been studied for its potential therapeutic benefits in treating mental health disorders and addiction.
Initially, LSD was intended to be a potential analeptic medicine and was synthesized to become a respiratory and circulatory stimulant. Little did its creator Albert Hofmann know that LSD would become a widely used and recognized recreational substance all over the world, partially fueling civil rights, anti-war, and the hippie movement in the 1960s.
Nowadays LSD has become one of the most known and popular psychedelics and is used recreationally all over the world. Users often report vivid visual hallucinations, synesthesia, and an intensified connection to nature, music, and art during an LSD trip, which can last up to 12 hours.
LSD used to be a widely researched substance in the ‘70s and ‘80s. In Albert Hofmann’s words, “LSD was used very successfully for 10 years in psychoanalysis,” he told the New York Times in 2006. “It should be a controlled substance with the same status as morphine.” And indeed, LSD has brought promising results for the treatment of depression, PTSD, anxiety, psychosomatic diseases, and addiction when used in clinical settings.
Even though LSD is currently illegal in most countries (but decriminalized in some), and most of the research has been shut down, recent studies on its therapeutic potential have prompted renewed interest in the substance as a tool for treating mental health. And who knows, perhaps in the future it will be one of the many ways to find healing, obtain personal growth, and explore the depths of the human mind with much more ease.
DMT / Ayahuasca: Journeying the Boundless Universe Within

This special compound has caused fascination all over the world for its ability to provide deep insights, spiritual breakthroughs, and lasting personal transformation, and has been commonly known as the ‘spirit molecule’.
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a powerful hallucinogen naturally found in certain plants and animals. While generally DMT is inhaled, Ayahuasca (a brew made from plants containing DMT) is traditionally ingested in shamanic rituals in the Amazon. The intense, immersive experiences induced by DMT and Ayahuasca have been reported to cause vivid visualizations, a deep sense of connection, and profound spiritual and mystical encounters with other beings and places. It seems that DMT truly allows us to travel through space and time, creating this immersive experience that can undeniably be overwhelming at times.
At the heart of the Amazon rainforest, ancient shamanic rituals have been practised for centuries, utilizing Ayahuasca as a sacred tool for spiritual exploration and healing. The ceremony typically takes place in a secluded and intimate setting, often within a circular structure. Participants gather around the shaman, who leads the ceremony with chants, prayers, and sacred songs known as icaros. These songs are said to invoke the spirit of the plants, guiding the participants through their journey and offering protection from negative energies.
Before the ceremony begins, the shaman prepares the Ayahuasca brew by combining the DMT-containing plant, usually the Banisteriopsis caapi vine, with a companion plant containing a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), such as the Psychotria viridis leaf. This combination allows for a prolonged and profound experience when ingested and can last anywhere from 4 to 8 hours depending on personal sensitivity, specific plant ingredients, and dosage.
Contrary to Ayahuasca, when DMT is inhaled, it produces an intense, short-lived experience that typically lasts around 5 to 15 minutes. The experience can be characterized by vivid visuals, encounters with otherworldly entities, and a sense of breaking through to an alternate reality.
Ibogaine: Breaking the Chains of Addiction

Ibogaine is a unique and powerful psychoactive substance extracted from the root bark of the Tabernanthe iboga plant, native to Africa. For centuries, indigenous cultures have utilized this remarkable compound in traditional ceremonies for purposes of healing, personal growth, and spiritual transformation.
In these ceremonies, ibogaine is typically ingested in the form of a bitter-tasting powder, which initiates a profound and often intense experience that can last anywhere from 24 to 48 hours. The ibogaine journey is characterized by vivid visions, introspection, and a deep connection with one’s ancestors and spiritual realms. Participants often gain profound insights into their lives, allowing them to confront and resolve emotional issues, traumas, and negative patterns.
In recent years, the therapeutic potential of ibogaine has gained increasing attention in the Western world, particularly in the field of addiction treatment. Evidence from studies suggests that ibogaine can help break the cycle of cravings and withdrawal from opiate, alcohol, and amphetamine addictions. In many cases, those who undergo therapy experience a ‘reset’ in their brain’s neuronal connections, opening a window of opportunity to finally overcome their addiction.
It is important to note that ibogaine treatment carries certain risks and is not suitable for everyone. The compound has been associated with potentially serious side effects, including cardiovascular issues, and should be administered under the supervision of trained professionals in a clinical setting. Proper screening, medical monitoring, and follow-up care are crucial to ensuring a safe and effective ibogaine therapy experience.
Mescaline: Discovering the Ecodelic World Within
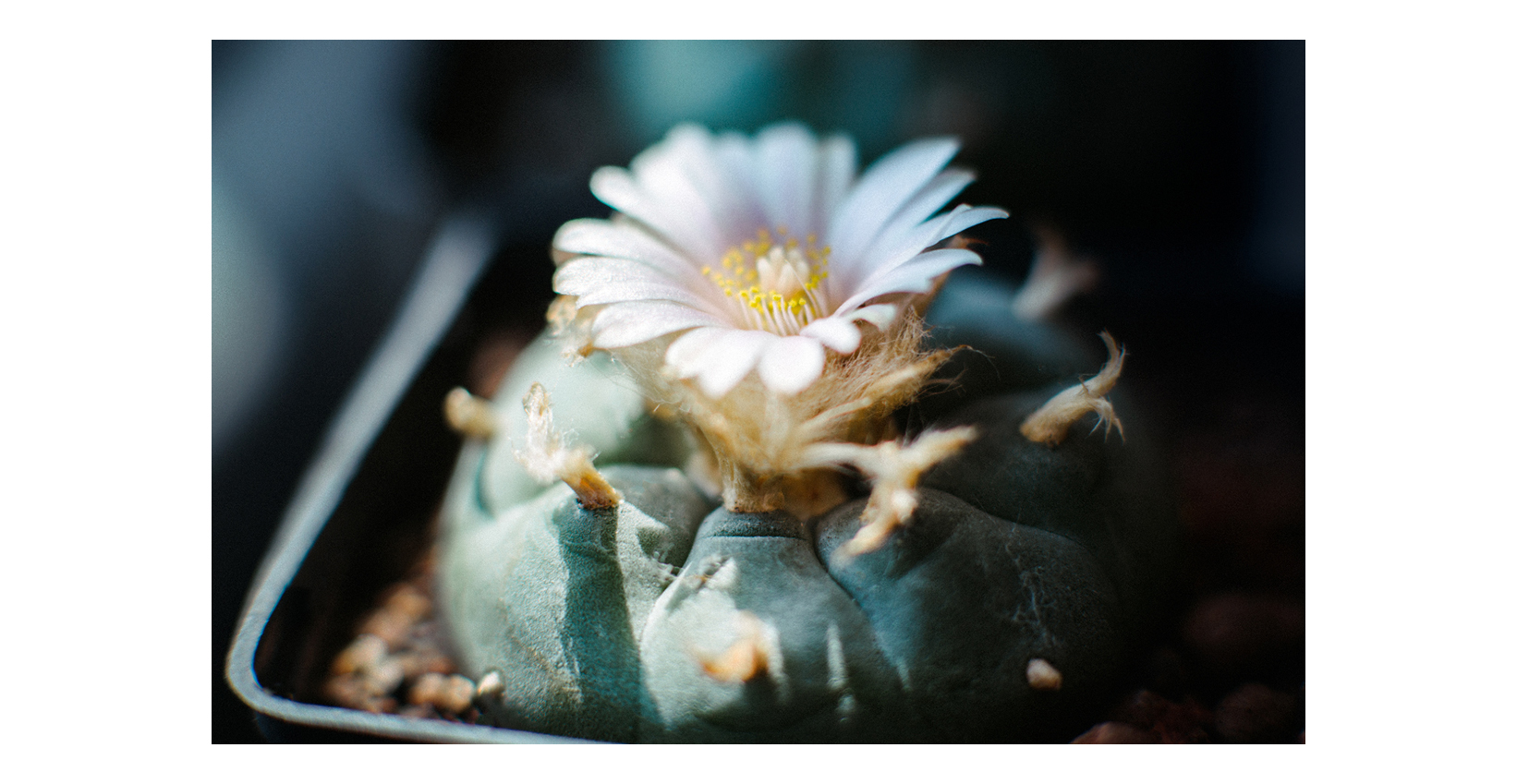

Mescaline is a potent psychoactive alkaloid found primarily in the peyote cactus (Lophophora williamsii) and other cacti species, such as the San Pedro cactus (Echinopsis pachanoi) and the Peruvian torch cactus (Echinopsis peruviana). It has held a sacred place in Native American cultures for thousands of years, revered for its visionary and introspective properties that facilitate spiritual exploration and healing.
The effects of mescaline typically begin within 1 to 2 hours after ingestion and can last up to 12 hours or more, depending on the individual and the dosage. Mescaline is known to induce a range of perceptual, emotional, and cognitive changes, including heightened sensory awareness, vivid hallucinations, and profound feelings of interconnectedness with the natural world. Many people who’ve experienced mescaline report that this psychedelic has a ‘grandfather’ energy to it: an old, wise, and forgiving nature.
Mescaline’s unique ability to evoke a sense of unity with the environment has led many to describe the experience as “ecodelic,” highlighting its potential for fostering a greater understanding of our relationship with the natural world and the importance of ecological stewardship. This connection with nature, combined with the introspective aspects of the experience, can result in profound personal growth and lasting positive change in one’s life.
Unfortunately, the cactuses are facing endangerment due to the growing interest in mescaline and other psychedelics, and hence the increasing demand for cacti species that contain the psychedelic compound. Peyote, the most well-known mescaline-containing cactus, is particularly vulnerable to endangerment. Peyote is a slow-growing cactus that can take years to mature. Overharvesting and habitat loss have led to a decline in wild peyote populations, threatening the sustainability of this sacred plant.
To address the endangerment of mescaline-containing cacti, a multi-faceted approach is needed, which includes conservation and habitat restoration efforts, sustainable harvesting practices, cultivation initiatives, legal protections, and public education campaigns. Working closely with indigenous communities and stakeholders, these solutions aim to preserve the ecological and cultural significance of these plants while ensuring their sustainability for future generations.
THC (Cannabis): Relaxation, Creativity, and Reflection

Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive compound found in cannabis, paints a vivid tapestry of effects on the human mind and body. While its potency may not be as grand in comparison to classic psychedelics, THC’s ability to evoke introspection, amplify sensory perception, and induce relaxation is undeniably present. In larger amounts, it can resemble psychedelic states and alter the perception of reality.
Throughout history, cannabis has certainly been one of the most popular psychedelics in various cultures, finding its way into traditional Indian and Ayurvedic medicine for its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and sedative properties, as well as the spiritual and religious ceremonies of Rastafarians and certain Hindu sects where cannabis was viewed as a sacred sacrament and considered a bridge to the divine.
THC has long been embraced for its recreational use, offering users an opportunity to unwind, socialize, and explore their inner selves. In recreational settings, THC induces a state of relaxation and euphoria, fostering a sense of connection among users. The recreational consumption of THC comes in various forms, including smoking, vaping, and edibles, and allows for a diverse range of experiences, providing a gateway to creativity, introspection, and shared enjoyment.
In recent years, the acceptance and use of THC in modern society have grown exponentially as researchers uncover its therapeutic benefits. THC has been found to be effective in reducing inflammation, easing symptoms of nausea and vomiting, particularly in chemotherapy patients, and helping to relax muscles, ease anxiety, depression, and effectively help manage PTSD symptoms.
As science further explores THC’s potential, its integration into modern medicine and wellness practices continues to expand, solidifying its role as a valuable therapeutic agent.
Salvia: A Gateway to an Unusual Reality

Salvia divinorum, a plant native to Mexico, has been used traditionally by Mazatec shamans for its powerful psychoactive effects. The active compound Salvinorin A can induce intense, short-lived experiences characterized by vivid hallucinations, altered perception of reality, and a sense of merging with objects or the environment.
It’s safe to say that not all experiences with salvia are positive or enlightening. For some users, the intense and disorienting nature of salvia’s effects can lead to terrifying and unsettling experiences. These challenging trips can be marked by feelings of fear, panic, confusion, or a sense of losing control. Users may also experience disturbing hallucinations, a feeling of being trapped in an alternate reality, or a disconnection from their own identity, leading to extreme discomfort and distress. The rapid onset and unpredictability of salvia’s effects can contribute to the difficulty in navigating these challenging experiences.
It seems, however, that the unpleasant experiences of salvia mostly stem from misunderstanding and misusing the plant. It’s been reported that smaller doses of salvia in relaxing and calm setting tend to offer anxiety-soothing effects and can be pleasant and mildly euphoric to experience.
Interestingly, the Mazatecs consumed salvia by either chewing the fresh leaves or making a liquid infusion. By doing so, they experienced a more gradual and controlled onset of the plant’s effects, as opposed to the intense, rapid onset that occurs when smoking dried leaves. They claimed that smoking salvia is foolish and does not do this plant justice. For them, it was important to establish a relationship with this plant and its spirit, and they treated it like a living entity that can provide them with guidance, spiritual insights, and wisdom when used correctly.
Although salvia is easily accessible and unregulated in many countries, there have only been a number of studies conducted to research its working mechanisms, effects, and potential therapeutic applications. To fully understand the potential and right form of application of salvia, more research is needed.
If planning to experiment with salvia, it is essential to approach it with caution and respect for its powerful psychoactive properties. Salvia being unregulated in many places can give the impression that the effects of this plant are mild, but that is not the case. Proper set and setting along with a supportive and experienced sitter can help reduce the risks of a negative experience. Additionally, starting with low doses can assist in managing the intensity of the experience.
LSA seeds: The Gentle Giant
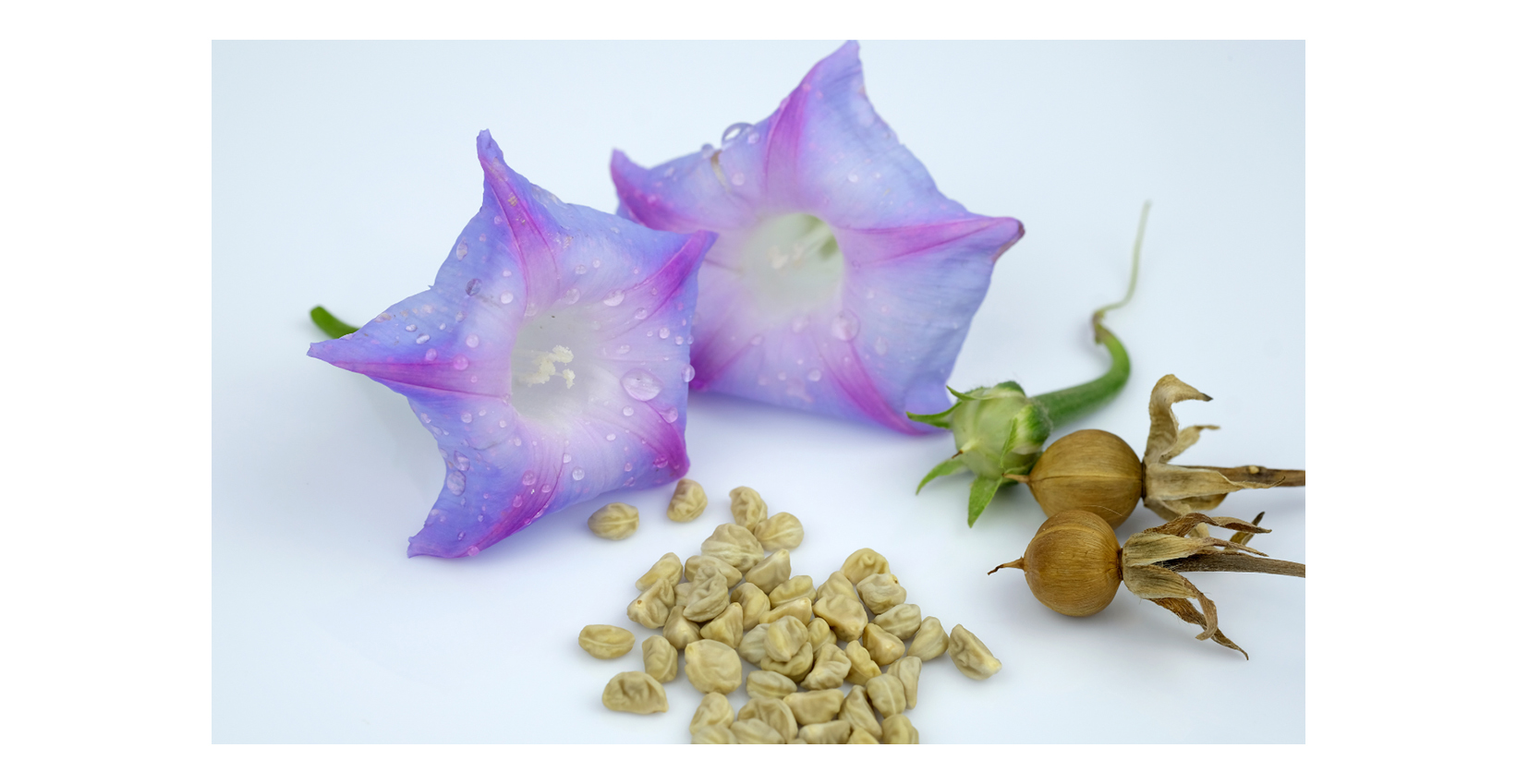

Lysergic acid amide (LSA), a naturally occurring psychedelic compound, can be found in several plant species, most notably in the seeds of morning glory (Ipomoea violacea) and Hawaiian baby woodrose (Argyreia nervosa). These seeds have a long history of traditional use in various indigenous cultures, particularly in Central America, where they were consumed for their entheogenic and visionary properties.
LSA’s chemical structure is similar to that of LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide), but its psychoactive effects are typically milder and more sedative in nature when taken in smaller amounts. Users often report feelings of introspection, visual distortions, and a heightened sense of connection with nature during an LSA experience. The effects can also include increased sensitivity to colors, textures, and sounds, as well as a sense of time dilation. Because of these effects, LSA seeds can be suited to use for meditation and introspection. An LSA seed trip can last anywhere from 8 to 12 hours.
While the LSA experience is generally considered to be more gentle than that of LSD (most likely because a bigger amount of seeds have to be consumed to achieve a similar effect), in larger amounts it can produce some unpleasant side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and muscle cramps, particularly when the seeds are consumed in large quantities. It is crucial to be cautious when using LSA seeds and keep in mind the dosage. It can be especially helpful to find LSA seeds that have been grounded into a fine powder and take them with a capsule. This will have a much gentler effect on the stomach and generally leave out the feelings of nausea and cramps.
Overall, LSA offers a natural psychedelic experience that has been valued for centuries by various cultures for its potential to induce introspection and a sense of connection with the natural world. As interest in the therapeutic potential of psychedelics continues to grow, further research into LSA and its potential benefits could yield valuable insights into its applications.
MDMA: From Recreational Fun to Therapeutic Catalyst
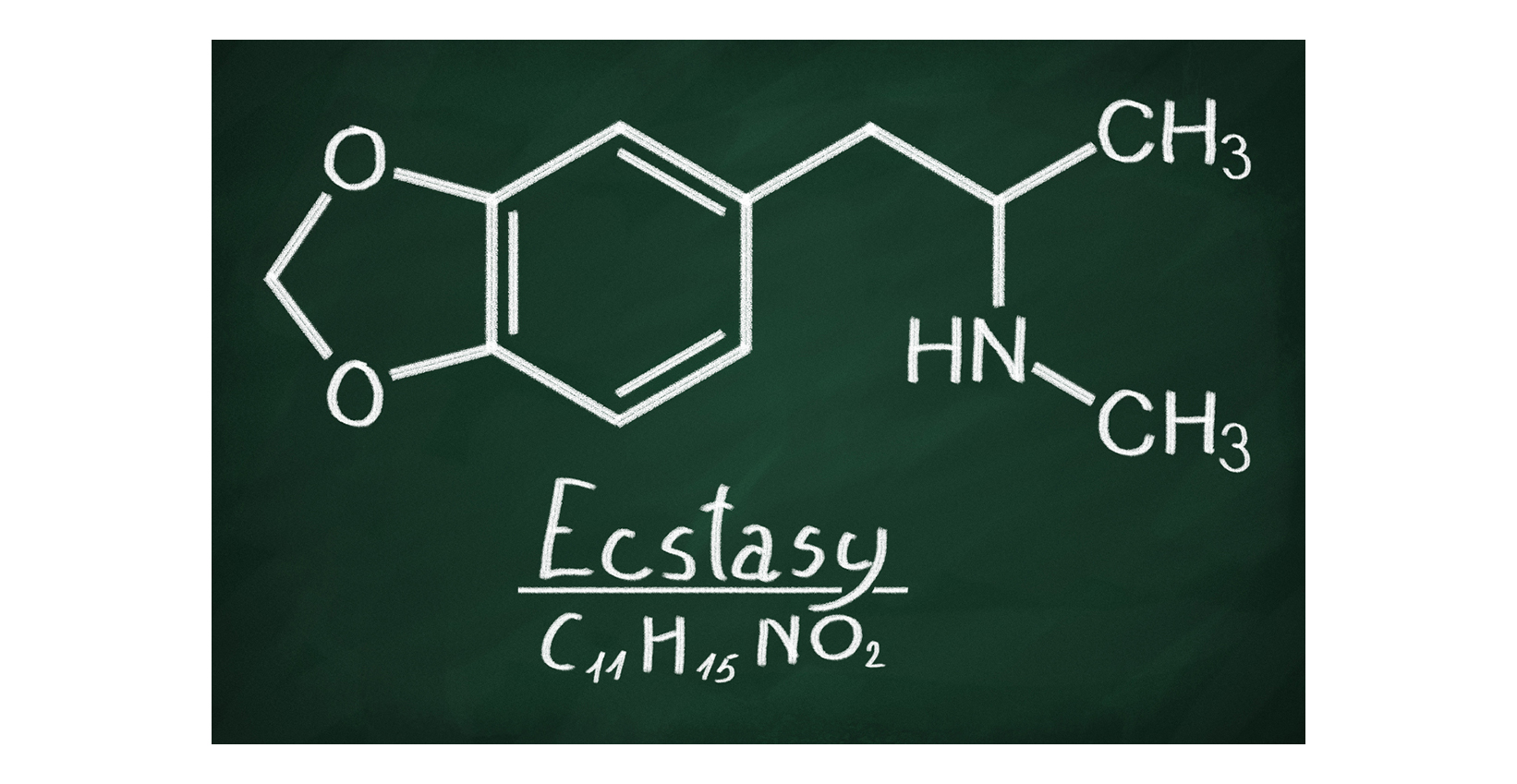
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), often referred to as ecstasy or molly, is a synthetic psychoactive substance that was developed in 1912. MDMA gained popularity in the 1970s and 1980s as a recreational substance due to its ability to induce euphoric and heightened sensory experiences, increase energy levels, and promote social bonding.
Even though MDMA is not considered a classical psychedelic, we would like to add it to this list as it shares some characteristics with psychedelics, such as alterations in perception and emotions. MDMA’s unique effects include feelings of empathy, love, and emotional openness. It works primarily by increasing the release of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain, resulting in its characteristic mood-enhancing properties. Users often report experiences of euphoria, emotional warmth, and a heightened sense of connection with others. Because of its effects, MDMA is certainly somewhere on the top of most popular psychedelics when it comes to recreational use.
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in the therapeutic potential of MDMA, particularly in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental health conditions. Clinical trials conducted by organizations such as the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS) have shown promising results, with participants experiencing significant reductions in PTSD symptoms and improved overall well-being following MDMA-assisted psychotherapy.
It is important to note that the therapeutic use of MDMA is carefully controlled and administered under the supervision of trained professionals in clinical settings. Recreational use of ecstasy or molly carries risks, as these substances are often impure or adulterated, and may result in adverse effects or dangerous interactions with other substances. MDMA is also strictly illegal in most countries in the world.
As research into the therapeutic potential of MDMA continues to expand, it holds the promise of transforming the way we approach mental health treatment and fostering a deeper understanding of the human psyche.
